
Many regions across the United States experienced “record-breaking high temperatures” in 2023 due to extreme heat, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Emergency room visits due to heat-related illness peaked in several regions in the U.S. and remained elevated for a prolonged duration compared to visits between 2018 and 2022, the agency’s recent Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report noted.
More males went to the emergency room for heat-related illnesses than females – especially those between 18 and 64 years old.
Americans are experiencing “longer, hotter and more frequent episodes of extreme heat,” the report states.
Is extreme heat a public threat?
“Extreme heat could be considered an invisible killer in so much as many people become exposed and vulnerable to its dangers quickly and often without warning,” Patrick McHugh, M.D., an emergency medicine physician at Cleveland Clinic Akron General in Akron, Ohio, told Fox News Digital.
Many regions across the United States experienced “record-breaking high temperatures” in 2023 due to extreme heat, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (iStock)
Although McHugh said Americans “shouldn’t worry,” he emphasized the need to “be aware and prepared for the dangers of heat waves.”
An EPA spokesperson told Fox News Digital, “As average temperatures rise due to climate change, the risk of extreme temperatures, heat waves and record-breaking temperatures increases.”
SUMMER MELTDOWNS: HERE’S HOW EXTREME HEAT CAN AFFECT YOUR MOOD AND MENTAL HEALTH
Here’s what to know about extreme heat and how to stay safe.
What is extreme heat?
“Extreme heat can be defined depending on a variety of factors, including location, weather conditions (such as cloud cover, humidity and temperature), and the time of year,” said an EPA spokesperson in an email.
It typically occurs when the weather is much hotter and/or more humid than average in a particular area, the agency added.
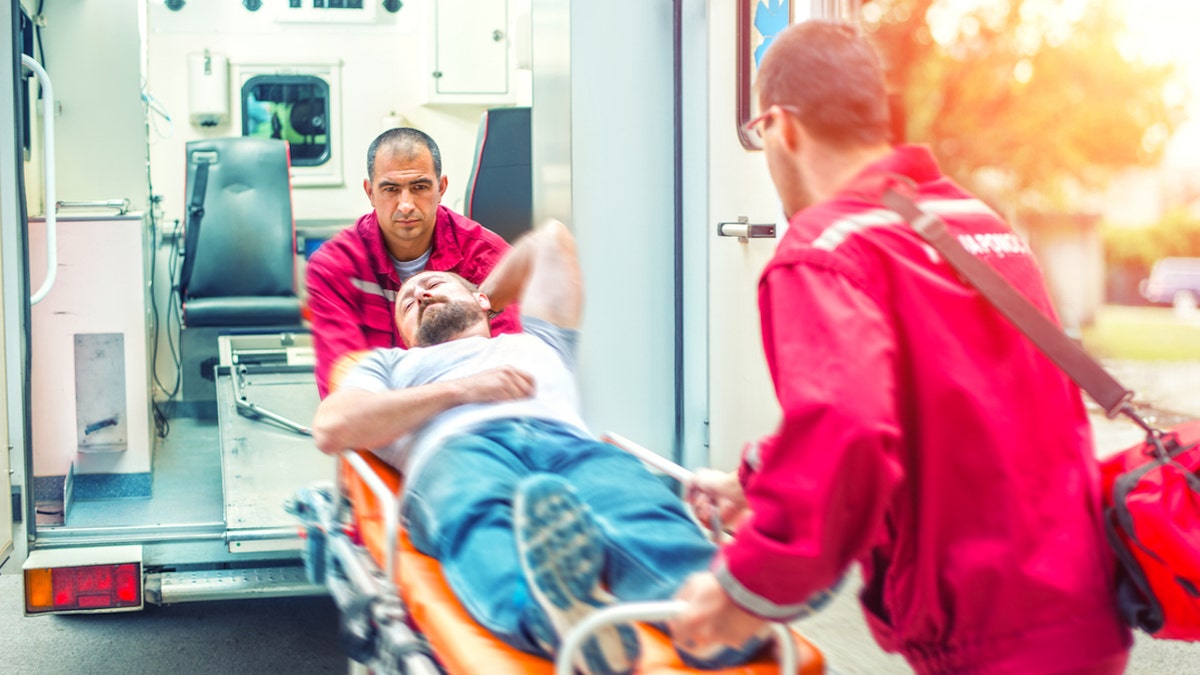

Emergency room visits due to heat-related illness peaked in several regions in the U.S. and remained elevated for a prolonged duration compared to visits between 2018 and 2022. (iStock)
While summertime temperatures of 100 degrees Fahrenheit might be normal for Phoenix, Arizona, for example — the same temperatures are considered extreme for Boston, Massachusetts.
“Where in the U.S. people are most susceptible to heat depends on what is normal for a given location and the type of infrastructure (such as access to air conditioning),” the EPA spokesperson noted.
“Extreme heat is becoming more common in places that have not historically experienced extreme heat … and don’t have the infrastructure to keep people cool, which has major consequences for health and safety.”
“Extreme heat could be considered an invisible killer … as many people become exposed and vulnerable to its dangers quickly and often without warning.”
A heat wave is typically defined as a “prolonged period of abnormally hot weather, usually lasting more than two days in a row,” the EPA spokesperson said.
Heat waves can occur with or without humidity.
The average global temperature has risen by more than 2 degrees Fahrenheit since the mid-1800s, according to McHugh.
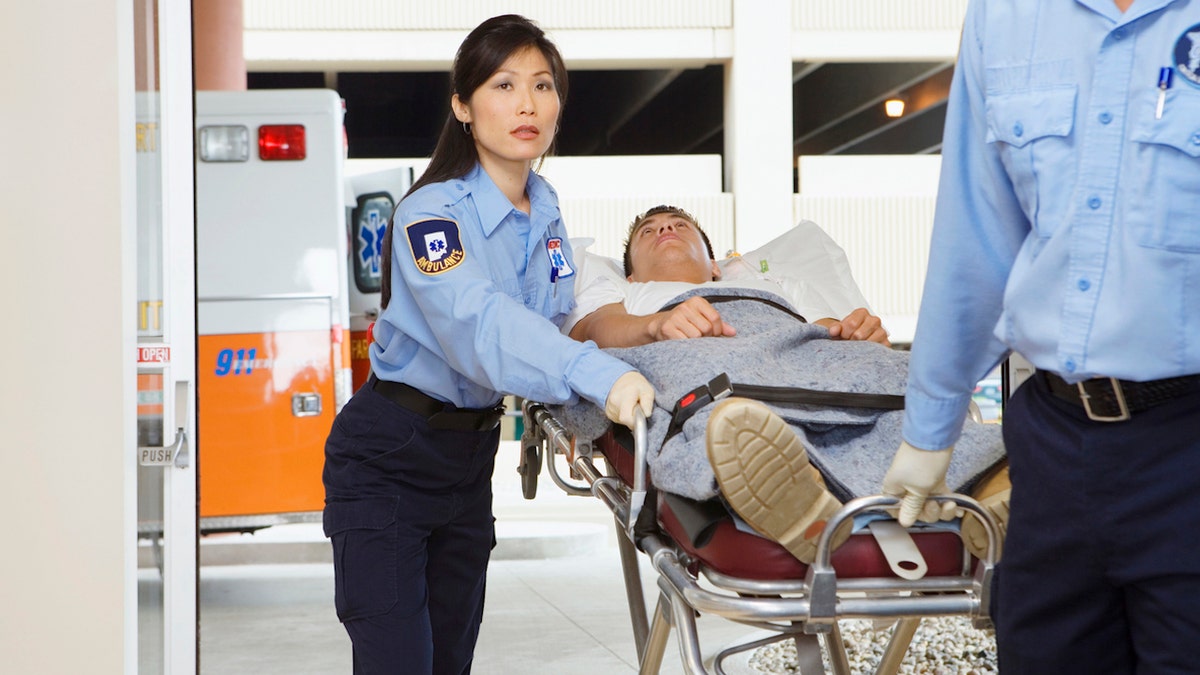

Elderly adults, infants, individuals taking certain medications and people with disabilities are at greater risk of heat-related illnesses. (iStock)
“This results in greater extreme heat temperatures, increased variability in temperatures and an increase in the risk of heat illness,” he told Fox News Digital.
The EPA’s Heat Waves indicator, which monitors trends in heat waves for 50 cities across the U.S. over the past 60 years, shows that heat waves are occurring more often over a longer period of time — both in average number of days and season length — and are also becoming hotter over time.
Risk factors for extreme heat effects
Elderly adults, infants, individuals taking certain medications and people with disabilities are at greater risk of heat-related illnesses, according to McHugh, who has a specialty in wilderness medicine.
These individuals may not have adequate resources to escape the heat and protect themselves, he warned.

“Extreme heat is becoming more common in places that have not historically experienced extreme heat … and don’t have the infrastructure to keep people cool, which has major consequences for health and safety,” an EPA spokesperson said. (iStock)
“Many schools in northern parts of the U.S. do not have air conditioning, so when heat waves happen in May/June or [in] September, students and teachers can be at risk,” the EPA spokesperson noted.
Certain factors can also increase someone’s risk of developing a heat-related illness, including fever, dehydration, prescription drug use, alcohol use or sunburn, according to the CDC.
NEW YEAR’S EVE BEVERAGE COULD GO EXTINCT DUE TO CLIMATE CHANGE, AI COMPANY PREDICTS
Healthy people can be at risk if they engage in strenuous physical activity when it’s very hot outside — which means it’s important to balance activities with actions that cool the body to prevent heat-related illness, the EPA advised.
Certain settings — such as inside cars, construction worksites and homes with little to no air conditioning — can also put people at greater risk, according to the CDC.
Heat island effect
Some urban areas experience higher temperatures compared to outlying areas.
“Structures such as buildings, roads and other infrastructure absorb and re-emit the sun’s heat more than natural landscapes like forests and water bodies,” the EPA spokesperson said.
These highly concentrated areas, which have limited greenery, become “islands” of higher temperatures relative to outlying areas.
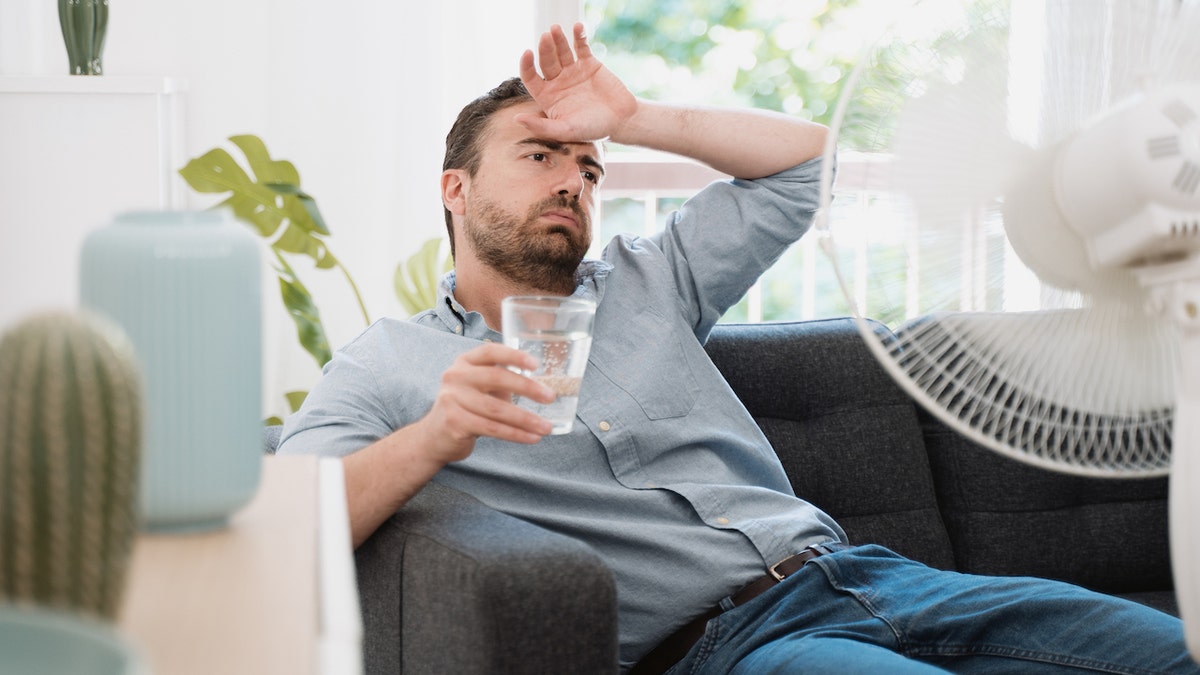

It’s important to balance activities with actions that cool the body to prevent heat-related illness, the EPA advised. (iStock)
“Daytime temperatures in urban areas are about 1 to 7 [degrees Fahrenheit] higher than temperatures in outlying areas, and nighttime temperatures are about 2-5 [degrees Fahrenheit] higher,” the agency noted.
People living and working in these areas are at higher risk of heat-related illness and death.
“Prolonged exposure to high temperatures is associated with increased hospital admissions for cardiovascular, kidney and respiratory disorders.”
As people lose control of their internal temperature amid extreme heat, they may experience a range of illnesses, including heat cramps, heat exhaustion, heat stroke and hyperthermia, according to the EPA.
“Prolonged exposure to high temperatures is associated with increased hospital admissions for cardiovascular, kidney and respiratory disorders,” the spokesperson said.
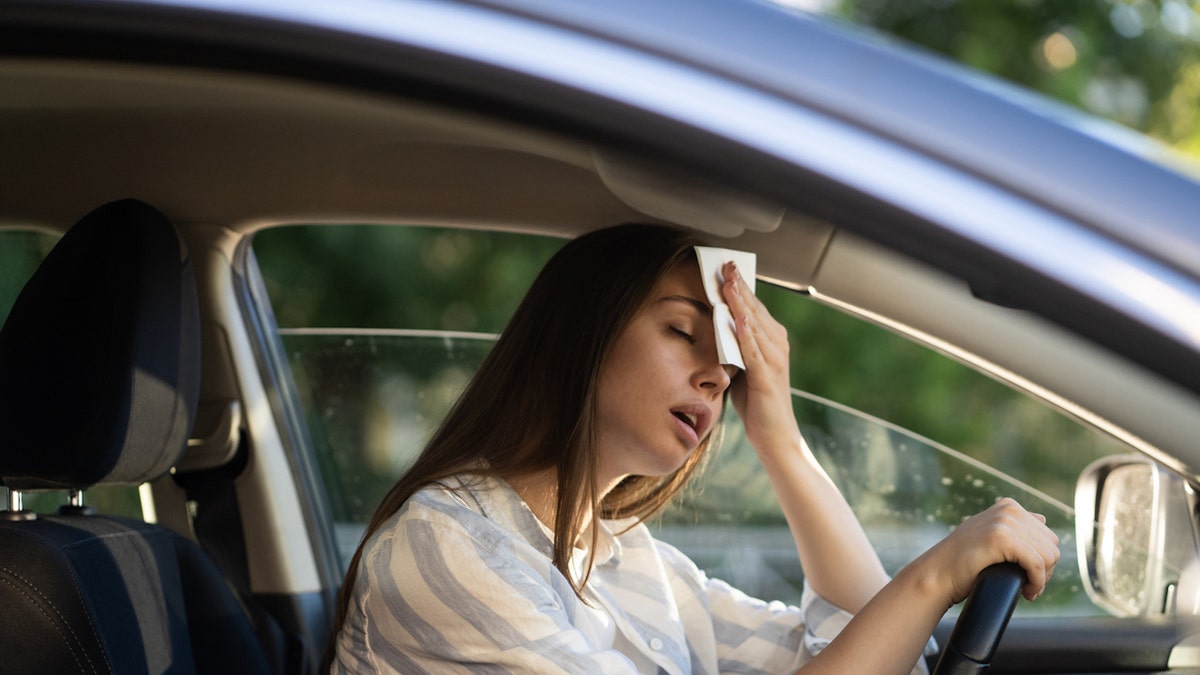

A particular setting can also place people at high risk, including inside cars, construction worksites and homes with little to no air conditioning, according to the CDC. (iStock)
Some 1,220 people die of heat-related illness every year in the United States due to extreme heat, per CDC estimates.
“Heat islands also increase energy demand for cooling, which can increase greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution and can be a financial burden for many people — particularly low- or fixed-income households,” the EPA spokesperson said.
HOT SUMMER SAFETY: HOW TO KEEP YOUR PETS HEALTHY IN EXTREME TEMPERATURES THIS SEASON
Everyone should have a plan in case of extreme heat, McHugh advised. “Either an air-conditioned home or building where shelter from the heat is easily available should be used.”
Extreme cold is dangerous, too
Those who counter climate change claims warn of extreme temperatures at both ends of the spectrum.
Most studies have shown that extreme cold causes about 10 times more excess deaths than extreme heat, according to William Happer, PhD, professor emeritus of physics at Princeton University in New Jersey and a prominent critic of climate extremism.
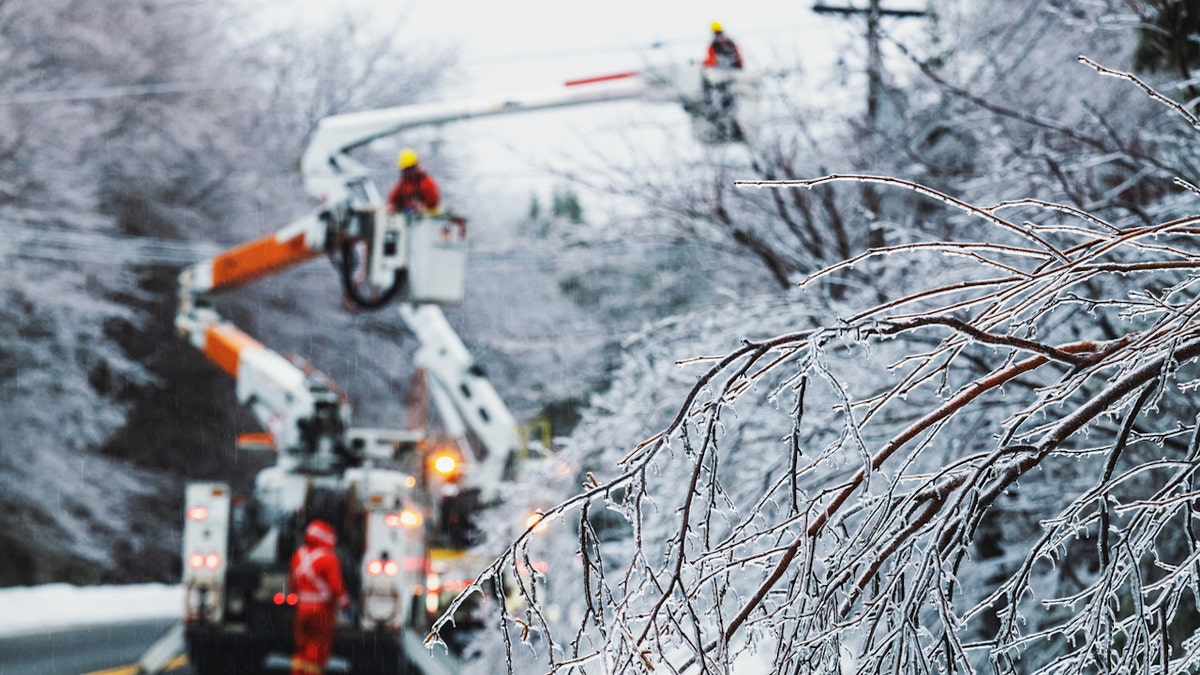

Most studies have shown that extreme cold causes about 10 times more excess deaths than extreme heat, according to a physics professor. (iStock)
A 2015 international study that analyzed deaths between 1985 and 2012 in 13 countries, including the U.S., found that most of the deaths due to adverse temperatures were attributable to cold weather.
The study, which was published in The Lancet, also revealed that most deaths were caused not by extreme temperatures, but by exposure to moderately hot and cold temperatures.
A more recent study published in The Lancet Planetary Health in 2021 found that for every death associated with heat, nine were connected to cold.
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
“No one knows how much of the modest recent warming, around 1 [degree Celsius] over the past century, has been due to greenhouse gases and how much is natural,” Happer told Fox News Digital.
He estimates that less than half of the warming is from increasing greenhouse gases.
“Whatever the cause, observations clearly show that there has been very little change in daily high temperatures,” Happer noted.
A more recent study published in The Lancet Planetary Health in 2021 found that for every death associated with heat, nine were connected to cold. (Credit: Fox News)
“The warming is almost all due to warmer minimum temperatures at night and in the winter.”
Compared to lives lost due to the extreme heat, the warming should have saved more lives that would have been lost because of the extreme cold, he said.
CLICK HERE TO GET THE FOX NEWS APP
For local heat and health information, the EPA spokesperson recommended using the CDC’s Heat and Health Tracker.
Americans can also visit their local National Weather Service (NWS) Forecast Offices for real-time heat-related warnings.
Fox Weather can also be consulted on a regular basis for up-to-date weather information and news.
For more Health articles, visit www.foxnews.com/health.




















